Green Belt
Practice
Exam
Questions
with
Answers
( In Green)
2
Q1: What method is used to increase confidence level in the results of a DOE ?
A Sequencing
B Replication
C Blocking
D Regression
Q2: If the correlation coefficient is between 0.5 to 1, it means there is a
A Negative correlation
B No correlation
C Positive correlation
D A&B
Q3: What is the best description of a hypothesis test?
A A tool for deciding if Statistical Significance exists between data
samples
B A tool for dissecting the data
C A tool for brainstorming
problems
D A tool for breaking up
the problem in smaller
parts
Q4: Which hypothesis test is similar to the 1 sample t-test but is used when the data
set is non-normal?
A 1- sample sign
B Kruskal-Wallis
C Friedman
D Mann-Whitney
Q5: Who is often called the ‘Father of quality control’?
A W. Edwards Deming
B F. Deming Edwards
C Dennis Edwards
D W. Frederick Deming
3
Q6: A typical linear regression equation would look like
A Yield = 100%
B Y = a + bx
C 3.4 = DPMO
D all of the above
Q7: Which one of the following would NOT be considered a COMMON CAUSE
VARIATION in a process? (choose the best answer)
A Serious workplace accidents that cause a shutdown for more than 2 hours
B Changes in the moods of customers every day that effect ticket sales
C Regular daily changes in average outside temperature that effect ice-cream sales
D The number of cars that pass a drive-through fast-food restaurant per hour during the
hours 12pm – 1pm each day
Q8: Which of the following activities is an example of non-value-added?
A Rework
B Inspection
C Packing
D Setup
Q9: What is the Japanese word for waste?
A Mode
B Muri
C Muda
D Mura
Q10: Which of these is NOT a Measure of Central Tendency or Position of a process?
A Inter Quartile Range
B Mean
C Mode
D Median
Q11: What is the middle value in a data set when arranged in numerical order?
A Variance
B Median
C Mean
D Mode
Q12: A Lean Six Sigma Green Belt practitioner constructs a control chart to display a
process mean and its outer limits. In such a chart, what does UCL stand for?
A Upper Control Length
B Upper Control Limit
C Upper Cycle Limit
D Upper Cycle Length
4
Q13: Which of the following is true about Control Limits and Specification Limits?
A Control limits are set by the customer
B Specification limits are set by the process owner
C It is best practice to set Control Limits narrower than Specification limits
D A suitable control chart and the right control limits will help to differential special
cause variation from common cause variation.
Q14: Which one of the following statements most accurately describes the following
string of numbers?
1.2, 1.4, 1.4, 1.8
A The mean is 1.45 and the SD approximately 0.22
B The mean is 1.44 and the SD is 0.685
C The mean is 1.1 and the SD is about 0.4
D The mean is 1.45 and the SD is 0.827
Q15: The p-value for a Moods Median test is 0.02 and the level of significance is set at
0.05, what decision is made?
A Use a different test
B Fail to reject null hypothesis
C Cannot determine
D Reject null hypothesis
Q16: What does SPC stand for?
A Standard Process Charting
B Statistical Process Control
C Standard Planning for Control
D System Performance Charting
Q17: A process with a process Sigma level of 6 over the long term would be expected
to produce which of the following?
A Approximately 3.4 defects per 1 Million Products
B Approximately 3.4 defects per 1 Million Defect Opportunities
C Approximately 3.4 defects per 1 Million Success Opportunities
D Approximately 3.4 defects per 1 Million Process Opportunities
Q18: In Lean Six Sigma, we generally consider 2 categories of variation in processes.
Which of the following are the correct 2 categories?
A Significant Variation and Practical variation
B Special Cause Variation and Common Cause variation
C Critical Cause Variation and Random Variation
D Significant Cause Variation and Low Variation

5
Q19: What is the minimum level of training that the member of a Lean Six Sigma process
improvement team requires ?
A Black Belt
B Master Black Belt
C Yellow Belt
D Green Belt
Q20: Value Stream Mapping is a technique that is considered to be part of the tool-kit
from which methodology?
A Kaizen
B Lean
C BPR
D Six Sigma
Q21: Understanding “the voice of the customer” is a technique used to provide
customers with :
A Cheaper products and services
B Buy one get one free offers
C Best in class quality
D Services and products that meet the customer expectations and needs
Q22: A product or service that does not meet the expectations of the customer is
called a
A Defective product or service
B Defect
C Problem
D Reject
6
Q23: It is always important to understand who is the customer of a process. Which of
the following is the best definition of ‘The Customer’?
A Anyone who supplies products or services to the process
B Stakeholders of the process
C Anyone who receives a product or service, or could receive a product of service from
the process
D People or groups who are responsible for the output of the process.
Q24: What Lean Six Sigma tool is used to organise and create order in the layout of
the tools and equipment in the workplace?
A SMED
B 5S
C Kanban
D Muda
Q25: The Lean Six Sigma concept called ‘Critical to Quality’ (CTQ) always focuses on
what?
A Reducing product variation
B reducing in-process inventories and minimizing product touch times
C Meeting the specific requirements of the customer
D Minimizing shipping damage

7
Q26: The name of an approved written plan of the expected benefits to the business
and the expected savings achieved from running a Lean Six Sigma project
is called a
A Project business case
B Project charter
C Savings document
D Project budget
Q27: What is the name of the technique used where a company measures its
performance against that of best-in-class companies?
A Run Chart
B Six Sigma
C Control Chart
D Benchmarking
Q28: What basic quality tools would be most applicable for a work team to use
when there is a need to follow procedures and work instructions more closely?
A Fishbone Diagrams and control charts
B Data sheets and histograms
C Pareto Charts and affinity diagrams
D Standard operating instructions and visual management
Q29: One of the purposes of using a fishbone diagram is to
A Define the problem in sequential order
B Show the relationship between parameters
C Identify the root causes of a problem
D Separate a problem into smaller components
Q30: Which of the following control charts would be best to use for a process in which
measurement data on a product is easily and inexpensively obtained?
A p-charts
B X-bar charts
C Median charts
D I-charts
Q31: Full Factorial and Fractional Factorial are both
A DOE designs
B OFAT designs
C Sigma designs
D Print designs
Q32: Which of the following is the best mathematical representation for a 2-level full
factorial designed experiment containing 4 factors?
A 2 x 4
B K
2
C 3
k
D 2
4

8
Q33: What is an experimental factor?
A A dependent variable
B An input variable for a designed experiment
C A metric of a process
D A standard deviation
Q34: A equation describes the relationship between a
Response Variable (Y) and a Predictor Variable (X)?
A Linear
B Correlation
C Regression
D Non-Linear
Q35: Which of the following statements is most true about Long Term process variation
compared to short term variation ?
A Long term variation contains all forms of variation in the process
B They are both the same
C Short term variation contains all forms of variation in the process
D Long term variation is always double (2 times) that of short term variation
Q36: Which of the following errors in a Hypothesis test is typically associated with a
"False Positive"?
A Depends on the experiments
B Type I error
C Type II error
D Type III error
Q37: Which item should not be identified in the Define Phase?
A Stakeholders
B Root causes
C The key problem area
D Business Case
Q38: Which of the following distributions is characterized by the Empirical Rule (68 /
95 / 99.7 rule)?
A Chi-square
B Normal
C Student’s test
D F statistic
Q39: In a brainstorming session, an effective facilitator should never:
A Encourage the participation of all members
B Dismiss ideas in the early stages
C Dismiss discouraging remarks
D Encourage adherence to a structure
9
Q40: How is takt time calculated?
A Available time divided by demand
B Demand divided by the amount of time available
C Time required for a task divided by demand
D Overall process time minus time required for a particular task
Q41: How many experimental runs would be required in a full factorial design if there are two (2)
levels and six (6) factors?
A 32
B 12
C 64
D 6
Q42: Which measure of a statistical distribution relates to how much it is equally
balanced on each side of the mode?
A Skewness
B Standard deviation
C Kurtosis
D Central tendency
Q43: All of the following are components of a multiple regression model EXCEPT:
A Blocks
B Correlation coefficients
C Residuals
D Intercept
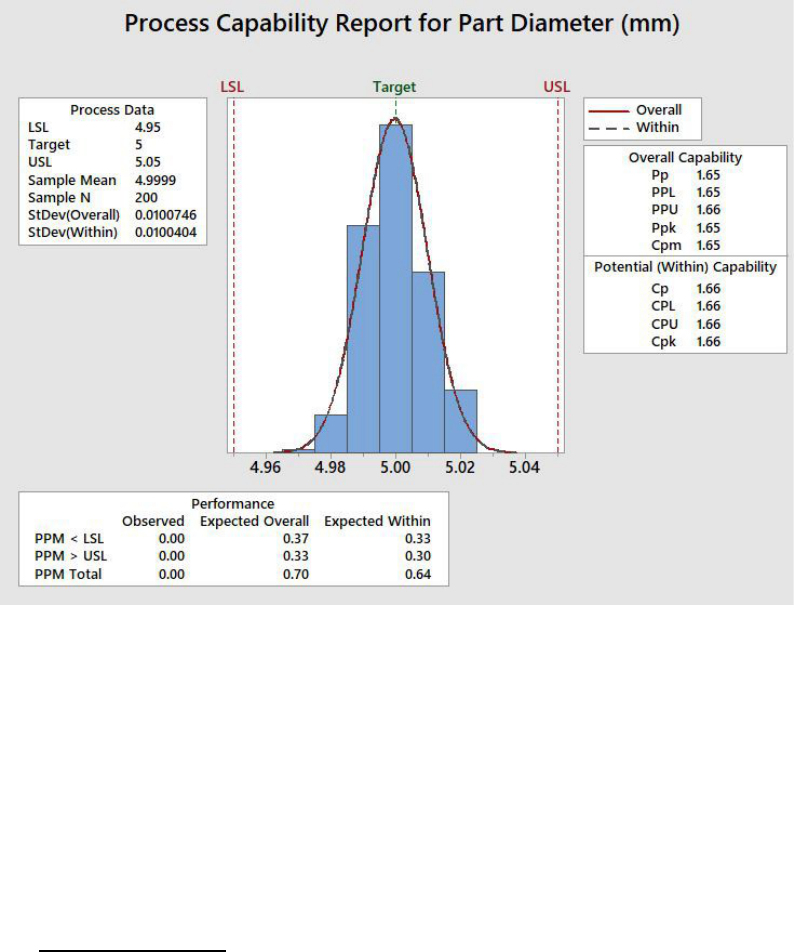
10
Q44: Which statement is correct about the Capability Analysis shown in Figure 1
(below)?
A There were 100 parts used in this capability study
B The Standard Deviation for part diameter is 0.00100746
C This distribution is Skewed.
D The upper specification limit is 5.05 mm
Figure 1:
Q45: Which statement is correct about the Capability Analysis shown in Figure 1
(above)?
A From this study we can predict that this process will produce less than 1 part per
million that are outside of the specification limits
B The process has a problem with centering.
C The parts have a mean average diameter between 4 mm and 4.9 mm
D The process needs significant improvements to be in control
Q46: Finish this sentence:
As part of Lean Six Sigma improvement in processes we aim to reduce the
“Batch and Queue” method of production and move towards a
method of production
A Single Team Flow
B Single Piece Flow
C Fluid Flow
D SPC

11
Q47: Which element of waste best describes the unnecessary movement of materials
and / or finished goods?
A Motion
B Inventory
C Transport / Conveyance
D Over processing
Q48: A technique used to dramatically reduce the time to change one tool set-up to
another is called
A Perfection
B SMED
C Overproduction
D Defect
Q49: Which of the 7 wastes identified by Taiichi Ohno describes the waste of a
downstream worker who cannot continue the next step of a process until a large
batch has finished processing in the upstream operation
A Over production
B Over processing
C Waiting
D Motion
Q50: Which of the following are considered to be the pioneers and “fathers” of
Quality Improvement and Statistical Process Control methods?
A Steve Jobs, Bill Gates
B Richard Branson, Alan Sugar
C Joseph Juran, W. Edwards Deming, Walter
Shewhart
D Jack Welch, Sam Walton
